Introduction to Antenna Polarization
In FPV drone systems, antenna polarization is one of the most critical yet frequently misunderstood aspects of RF signal transmission. Whether you’re a racing pilot needing reliable video through tight courses or a long-range enthusiast pushing distance limits, understanding polarization – particularly circular polarization – can mean the difference between crystal-clear video and frustrating signal breakup.
This comprehensive guide will explain:
- The fundamental differences between RHCP and LHCP
- Why circular polarization dominates FPV applications
- How reflections affect your signal (including the truth about parabolic dishes)
- Real-world antenna recommendations from ProDrone.pl
- Advanced setup tips for optimal performance
Understanding Polarization Basics
Linear vs Circular Polarization
All radio waves have polarization – the orientation of their electric field oscillation:
Linear Polarization:
- Electric field oscillates in a single plane (vertical or horizontal)
- Examples: Dipole antennas, Moxon antennas
- Advantages: Simple design, good for control links
- Disadvantages: Sensitive to antenna orientation changes
Circular Polarization:
- Electric field rotates as the wave propagates
- RHCP (Right Hand Circular Polarization): Clockwise rotation
- LHCP (Left Hand Circular Polarization): Counter-clockwise rotation
- Advantages: Maintains signal integrity during drone maneuvers
Why FPV Systems Favor Circular Polarization
FPV video systems overwhelmingly use circular polarization because:
- Orientation Independence: Drones constantly change attitude – circular polarization maintains signal regardless of roll/pitch/yaw
- Multipath Rejection: Naturally filters out reflected signals (more on this later)
- Interference Reduction: Allows multiple pilots to fly simultaneously with less crosstalk
RHCP vs LHCP: Key Differences
There’s no performance difference between RHCP and LHCP when used correctly.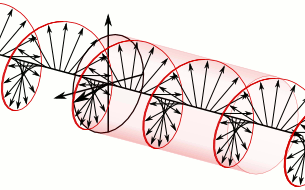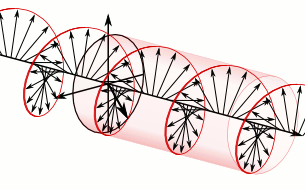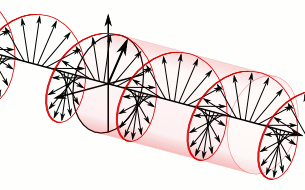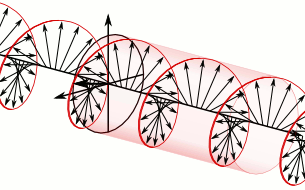
While RHCP and LHCP are functionally identical in performance, their opposite rotation has important implications:
| Characteristic | RHCP | LHCP |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation Direction | Clockwise | Counter-clockwise |
| Common Applications | Standard FPV, GPS | Alternate channel systems |
| After Reflection | Becomes LHCP | Becomes RHCP |
| Compatibility | Must match RX/TX | Must match RX/TX |
Critical Rule: Your video transmitter and receiver must use the same polarization type (both RHCP or both LHCP) for optimal performance.
The Reflection Paradox: How Surfaces Affect Polarization
This is where many pilots get confused – especially regarding parabolic dishes.
The Fundamental Principle:
All reflections reverse circular polarization:
- RHCP → LHCP when reflected
- LHCP → RHCP when reflected
This occurs because the reflection inverts the wave’s rotation direction.
Flat Surface Reflections:
When your signal bounces off the ground, buildings, or trees:
- Direct signal maintains original polarization
- Reflected signal reverses polarization
- Matching RX/TX polarization automatically rejects reflected signals
Parabolic Dish Truth:
Despite common misconceptions:
- Parabolic dishes DO reverse polarization just like flat surfaces
- The curved shape focuses the signal but doesn’t prevent polarization reversal
- You must account for this in your antenna selection
Dish Setup Rule:
If using a parabolic reflector:
- VTX antenna: RHCP
- Dish receiver antenna: LHCP (to match the reflected signal)
ProDrone.pl Antenna Recommendations
RHCP Solutions (Standard FPV)
- ProDrone PRO 12T (RHCP)
- Premium omnidirectional antenna
- Optimized axial ratio for clean signal
- Ideal for freestyle and racing
- Helix PRO 18 (RHCP)
- High-gain directional antenna
- Perfect for long-range applications
- 18dBic gain for extreme distances
LHCP Solutions (Specialized Applications)
- LHCP Crosshair 5.8GHz
- Rejects RHCP interference
- Excellent for group flying
- Works with dish reflector systems
- LHCP Helical Array
- Custom ground station solution
- Pairs with parabolic reflectors
- 14dBic gain for weak signal reception
Linear Antenna Options
- Moxon 2.4GHz (Linear)
- Highly directional
- Ideal for control links (ELRS/Crossfire)
- Not for video transmission
Advanced Setup Considerations
Group Flying Protocol
When multiple pilots fly together:
- Alternate polarizations between pilots
- Example: Pilot 1: RHCP, Pilot 2: LHCP
- Reduces video crosstalk and interference
Polarization Purity Matters
Not all RHCP/LHCP antennas are created equal. Key specifications:
- Axial Ratio: Measures how “pure” the circular polarization is (closer to 0dB is better)
- VSWR: Indicates how well the antenna is tuned (under 1.5:1 ideal)
ProDrone.pl tests all antennas for optimal performance in these metrics.
Special Case: Dual-Polarization Systems
Some advanced systems use:
- Simultaneous RHCP/LHCP reception
- Diversity combining for maximum signal robustness
- Requires specialized receivers and antennas
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Problem: Video breakup when flying behind obstacles
Solution: Ensure matched polarization and consider higher-gain antennas
Problem: Interference from other pilots
Solution: Switch to opposite polarization scheme
Problem: Weak signal with dish system
Solution: Verify you’re using opposite polarization on receiver
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
- RHCP and LHCP are equally effective – consistency matters most
- All reflections reverse polarization – including parabolic dishes
- Dish systems require opposite polarization on receiver
- Group flying benefits from mixed polarization
- Antenna quality (axial ratio, VSWR) significantly impacts performance
At ProDrone.pl, we offer professionally tuned antennas for every FPV scenario. Our technical team can help you select the perfect polarization solution for your specific needs.
You can find more detailed information on wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_polarization
